Your credit score has always played a pivotal role in your financial health, but in 2025, it’s more important than ever. As digital banking, AI-driven risk assessments, and new regulatory frameworks reshape the lending landscape, lenders are relying heavily on credit scores to determine loan eligibility, interest rates, and terms. Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, car loan, personal loan, or business credit, understanding how your credit score influences your chances is crucial.
This comprehensive guide explores the evolving impact of credit scores on loan approvals in 2025. We’ll look at how credit scores are calculated, what factors influence them, and how lenders use them to make critical decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Credit scores remain a critical factor in loan approvals in 2025.
- AI, open banking, and alternative data sources are modernizing credit assessments.
- Scores above 750 yield the best terms; below 600 often face obstacles.
- Responsible behavior—timely payments, low utilization, monitoring—is key.
- Understanding and improving your score gives you more financial power.
What Is a Credit Score?
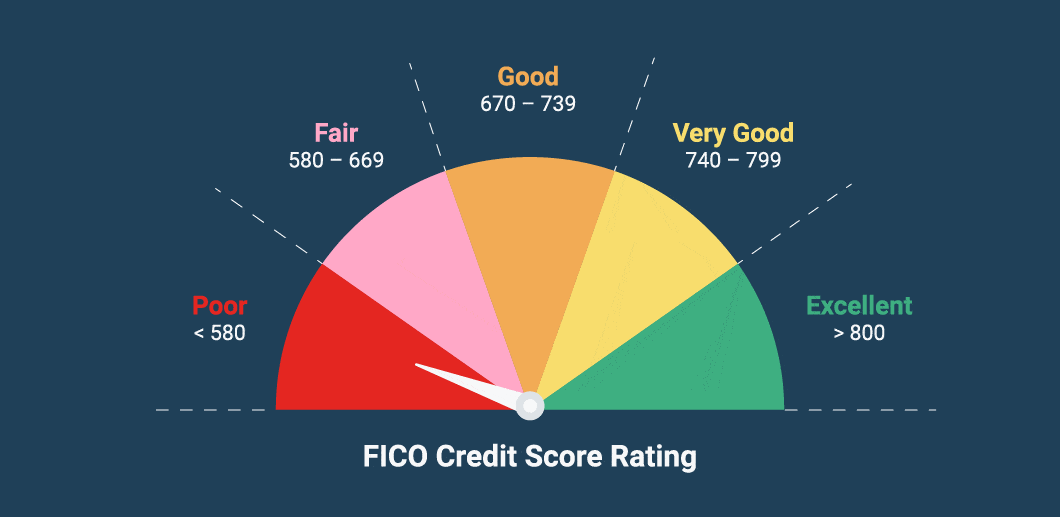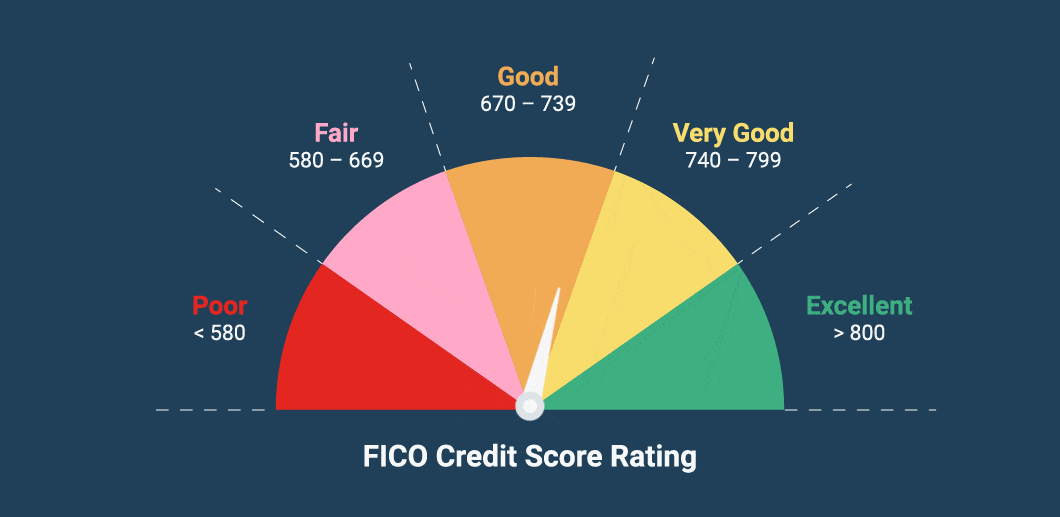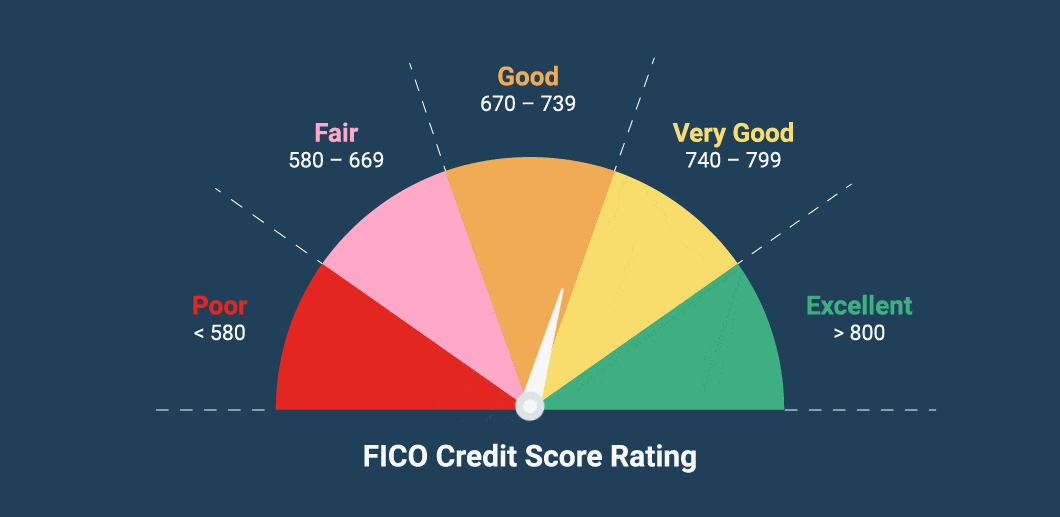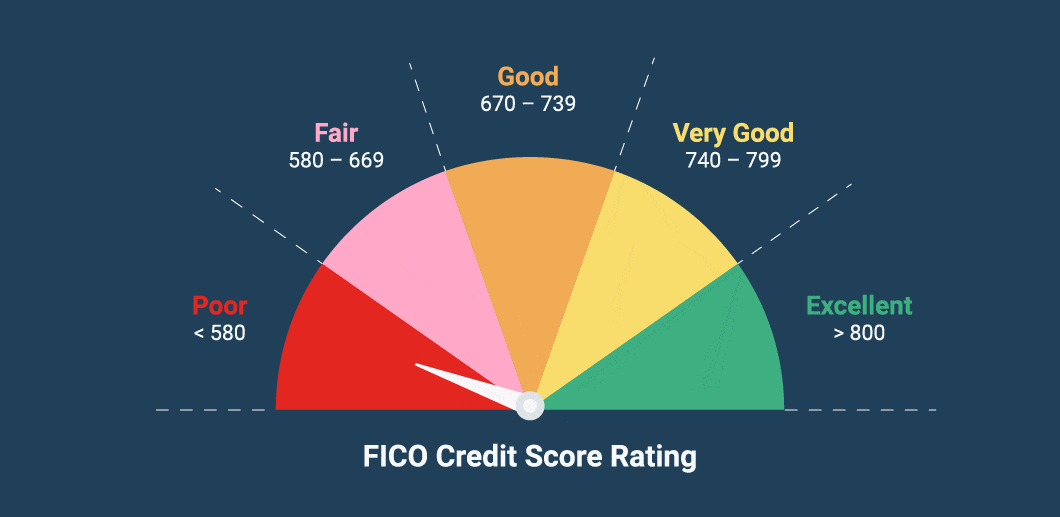
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, typically ranging from 300 to 850. It’s derived from your credit history, including your payment behavior, outstanding debts, credit mix, and length of credit history. In 2025, most scores are calculated using updated algorithms from FICO 10 and VantageScore 5.0, integrating alternative data and machine learning.
How Credit Scores Are Calculated in 2025
In 2025, the primary components of a credit score remain similar but are now supplemented with more real-time data:
- Payment history (35%): Timely payments on credit cards, loans, and bills.
- Credit utilization (30%): The ratio of your credit card balances to limits.
- Length of credit history (15%): How long you’ve had credit accounts.
- Credit mix (10%): A variety of credit types—loans, cards, retail accounts.
- New credit (10%): Recent inquiries and newly opened accounts.
New models now include:
- Cash flow and banking behavior: Tracked through open banking.
- Rent, utility, and subscription payments: When reported, they boost thin credit profiles.
- Employment and income patterns: Verified via secure financial APIs.
How Credit Scores Affect Loan Approvals
Loan Eligibility
In 2025, automated underwriting systems screen loan applications based on your credit score within seconds. A higher score improves the chances of pre-approval and reduces the need for manual verification.
Interest Rates
Credit score bands heavily influence the interest rates offered. For instance:
- 750+: Best interest rates.
- 700-749: Competitive rates.
- 650-699: Moderate interest rates.
- 600-649: Subprime rates.
- Below 600: High interest or outright denial.
Loan Terms and Limits
Higher scores also unlock better repayment terms, higher loan limits, and lower down payments. Lenders view high scores as indicative of lower risk.
Collateral and Documentation
Applicants with lower scores may be required to submit additional documentation or offer collateral to mitigate risk.
Emerging Trends in 2025

- AI-Powered Risk Models: Lenders are using AI to identify patterns beyond traditional credit data, improving access to underserved populations.
- Alternative Data: Including rent, utility, and mobile phone bills helps evaluate non-traditional credit behavior.
- Personalized Lending Offers: Based on credit profiles, borrowers receive offers tailored to their financial situations.
How to Improve Your Credit Score in 2025
- Pay All Bills on Time: This remains the most important factor.
- Keep Credit Utilization Below 30%: Preferably around 10%.
- Use Experiential Data: Consider services that report rent, streaming, and utility payments.
- Avoid Unnecessary Hard Inquiries: Space out applications.
- Monitor Your Report Regularly: Use free or paid tools to catch errors and fraud.
- Dispute Errors Promptly: Even a small inaccuracy can impact your score.
Credit Score and Loan Type
| Loan Type | Ideal Score Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mortgage | 680+ | Lower scores need higher down payments |
| Auto Loan | 660+ | Subprime rates for scores under 600 |
| Personal Loan | 640+ | Many lenders now offer AI-based scoring |
| Business Loan | 700+ | Requires business credit and personal score |
| Student Loan | 620+ | Government loans less score-dependent |
Also Read : Top 5 Tips For Getting The Best Home Loan Rates In 2025
Conclusion
In 2025, your credit score is more than just a number—it’s a gateway to financial opportunities or barriers. As technology and financial services evolve, so too does the way your credit score is calculated and used. Staying informed, actively managing your credit profile, and understanding lender expectations can make all the difference in your financial journey. Whether you’re rebuilding credit or maintaining a high score, your efforts can significantly impact your access to loans, interest rates, and overall financial wellness.
FAQs
What is considered a good credit score in 2025?
A good credit score in 2025 typically falls between 680 and 749. Scores above 750 are considered excellent and receive the best loan terms.
Can I get a loan with a low credit score?
Yes, but your interest rates may be higher, and you might need to provide additional documentation or collateral.
How often should I check my credit score?
You should check your credit score at least once a month to monitor changes and detect fraud early.
Do soft inquiries affect my credit score?
No, soft inquiries do not impact your credit score. Only hard inquiries, such as loan or credit card applications, may lower it slightly.
How long do negative marks stay on my credit report?
Most negative marks remain for 7 years, but bankruptcies can stay for up to 10 years.
Will paying off a loan improve my credit score?
Yes, especially if the loan was paid on time and in full. It shows responsible credit behavior.
How does AI impact credit scoring in 2025?
AI analyzes a broader range of data points, including spending habits and employment trends, providing more accurate and inclusive credit evaluations.

